HIV is often known as a silent killer but if you’re paying attention, these are the early symptoms that you need to watch out for. If you have an active sex life or think you may have been exposed to HIV, it is important that you get tested as soon as possible. Here are some common symptoms of HIV in men that may alert you that something is wrong.
Many people experience severe flu-like symptoms which are the body’s natural response to the virus and are an indicator that you may have been exposed to something sinister.
Four phases of an HIV infection:
Time is of the essence. Getting yourself tested and beginning treatment immediately ensures that you keep your immune system intact as much as possible. Getting treated with HIV medications will also practically eliminate your chances of transmitting your HIV to others.
Phase 1: the acute infection
The acute phase of an HIV infection lasts two to eight weeks after the initial moment of infection. HIV replicates itself very quickly in your body, even if your body has not even started making antibodies against the virus. Within two weeks your viral load will rise to a million or more virus particles.
Read more: Baby upper teeth first myths you should know : Nigerian Culture
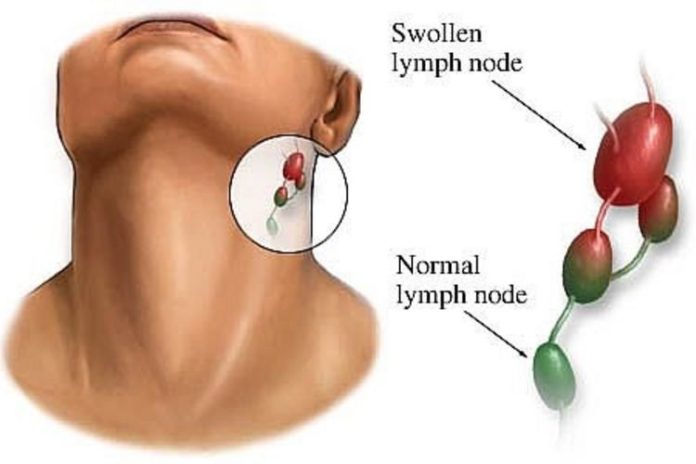
Symptoms of an acute HIV infection
A couple of weeks after you have been infected with HIV, the amount of HIV in your body will have increased significantly and your immune system will be activated. You could get flu-like symptoms. Symptoms that typically accompany an acute HIV infection are:
Most people who are infected with HIV will get symptoms in the acute phase. Those are not always recognized as being symptoms of HIV, however, and they normally last two weeks, but they could last anywhere from a few days to ten weeks.
Be alert to symptoms of HIV after having had risky sex
If you have run a risk, for example, because you didn’t use a condom or because the condom broke, be on the lookout for symptoms in the coming weeks. If you have flu-like symptoms or any of the symptoms described above, be aware that it could be HIV and when you visit your doctor or the clinic, make sure you tell them the following:
Phase 2: recent infection
This period follows the acute infection and lasts for about six months after the initial infection.
The flu-like symptoms mentioned earlier could also appear in this period.
Phase 3: latent/chronic HIV infection
The length of this phase varies with each person. With some people it could last a year; with others, it could last 15 years. It depends on how aggressive the virus is and how strong your immune system is.
Symptoms of a latent/chronic HIV infection
The symptoms you get in this phase will often last longer than they do in the acute phase. Symptoms in this phase include:
Symptoms of AIDS
The diagnosis of “AIDS” is only given if HIV has damaged your immune system to such an extent that you become ill from an infection that your body would normally have been able to fight off.
A wide range of serious medical conditions will present themselves. A few examples:
When faced with the prospect of AIDS, it will always make sense to get treated. Thanks to the treatment, “AIDS” is a stage that you never have to reach. It will take longer before your immune system gets back to strength, however.